
"A piece of perfect quicklime, made from two drams of chalk, and which weighed one gram and eight grains, was reduced to a very fine powder, and thrown into a filtered mixture of an ounce of a fixed alkaline salt and two ounces of water. In 1752, he wrote the following, which will be explained below: Joseph Black (1728-1799) made extensive studies of the carbonates of the alkali and alkaline earth metals and is considered the discoverer of carbon dioxide (which he called "fixed air"). "Men should frequently call upon nature to render her account that is, when they perceive that a body which was before manifest to the sense has escaped and disappeared, they should not admit or liquidate the account before it hs been shown to them where the body has gone to, and into what it has been received." "Wrongly do the Greeks suppose that aught begins or ceases to be for nothing comes into being or is destroyed but all is an aggregation or secretion of pre-existing things so that all becoming might more correctly be called becoming mixed, and all corruption, becoming separate." In addition, he was certainly not the first to accept this law as true or to teach it, but he is credited as its discoverer. However, philosophical speculation and even some quantitative experimentation preceeded him.

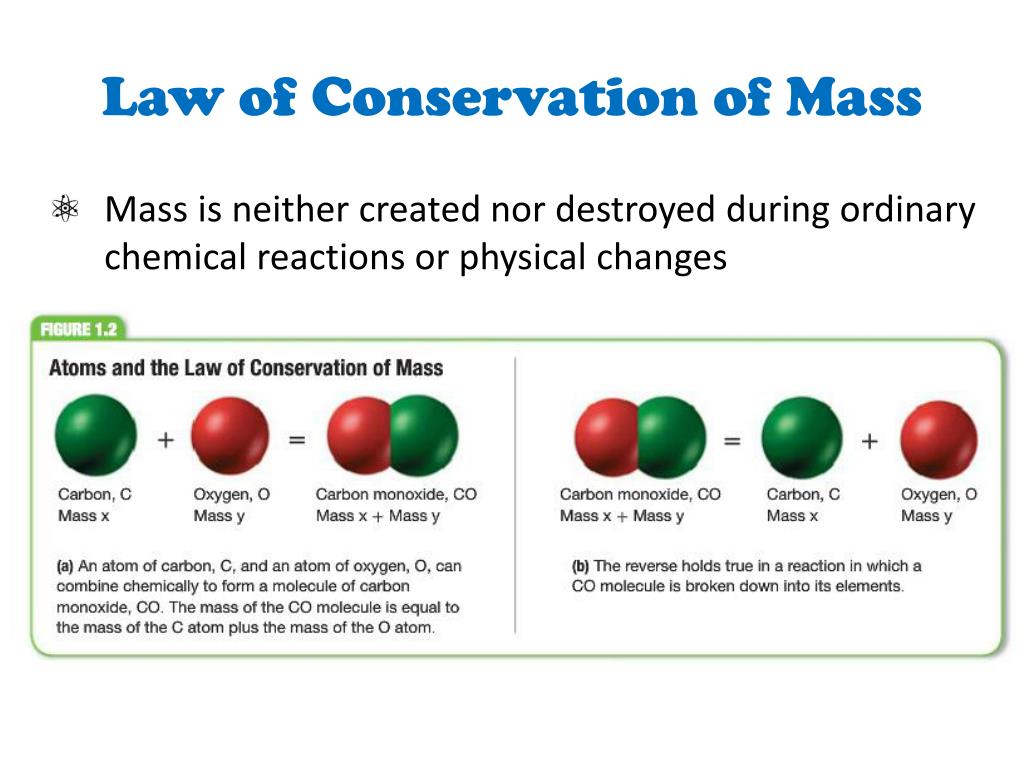
It was discovered by Antoine Laurent Lavoisier (1743-94) about 1785. In a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. The Law of Conservation of Mass (or Matter) in a chemical reaction can be stated thus:

How to balance a modern chemical equation
The meaning of a modern chemical equation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
